Utilizing AI’s Tax Filing and Processing Efficiency
- August 5, 2025
- 0

Annually, a glut of returns from individuals who file their income taxes at the last minute overwhelm many state and local tax agencies. AI, on the other hand, is being used by some to streamline and reduce costs. It should come as no surprise that tax departments are turning to AI tools to speed up and improve tax filing, processing, and compliance now that AI is present in every industry. To automate the extraction and classification of data from various tax forms, Taazaa, for instance, developed a bespoke AI tax filing assistant for an Ohio municipality. The system is integrated with the city’s core systems to enhance efficiency.
Similar AI systems are used by corporate accountants to automate complicated tax compliance and reporting tasks, carry out intricate calculations and analyses, and locate potential opportunities for tax planning. Even the IRS is starting to use artificial intelligence to improve return processing and help expose tax evasion and fraud. Additionally, they are introducing an AI agent to assist IRS employees in finding complex taxpayer inquiries quickly. However, AI tax solutions face difficulties and limitations, particularly with regard to the security and quality of the data. This article explores the advantages and drawbacks of AI tax processing solutions.
Contents
The Increasing Role of AI in Tax Processing
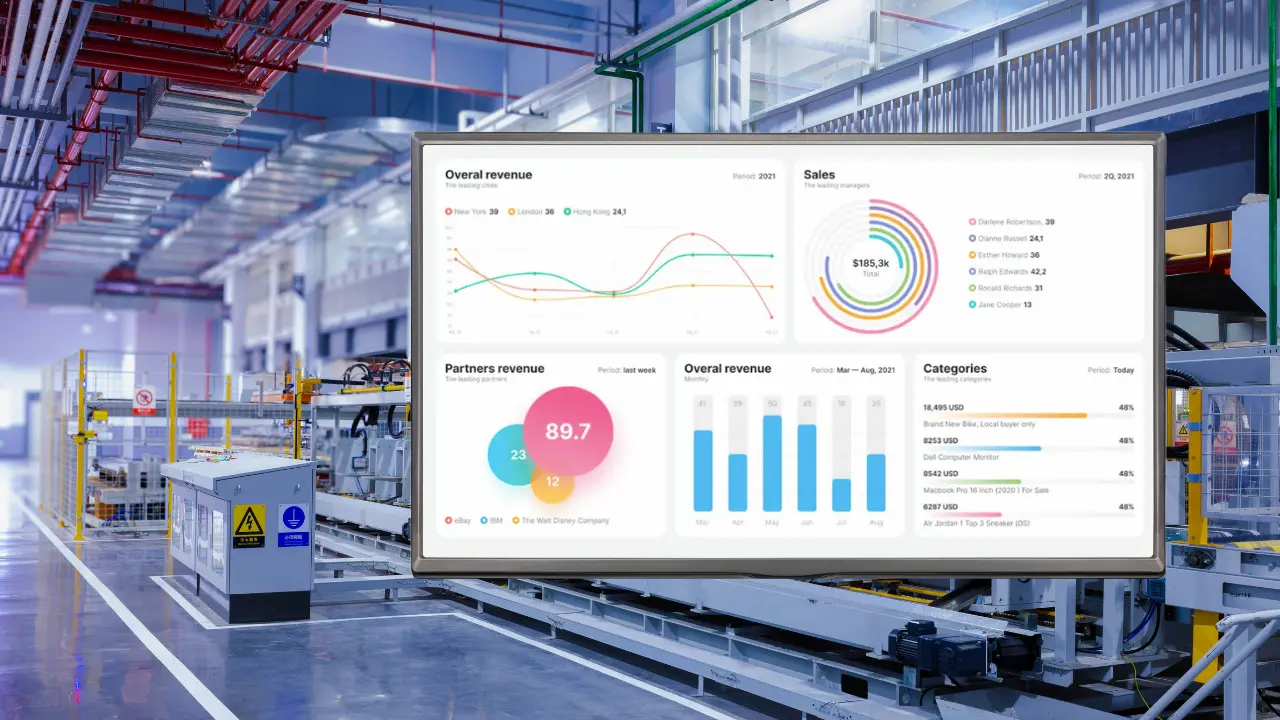
Tax authorities nationwide increasingly recognize AI’s potential for enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of tax return processing and improving overall tax administration.
Earlier this year, Deloitte published a report based on a survey of 1,000 tax and finance leaders and a series of interviews with multinational heads of tax. According to that report, “tax and finance leaders are focusing on data, compliance cost management, automation, and, increasingly, AI,” Rising to Meet the Moment: Tax Transformation Trends 2025. For instance, over the next two years, 45 percent of tax leaders will seek AI specialist skills. In addition, 42% said data analytics and data-driven strategic insights, and 36% identified specialist tax technical skills. AI is connected to all three of these skill sets. Ralf Pieters, Head of Tax at AzkoNobel and one of the respondents to the survey, stated, “Everybody knows that if you want to stay relevant within Tax, you need to master AI.”
Keeping up with the requirements of the law Globally
More stringent reporting requirements, such as OECD Pillar Two disclosures and real-time tax data access, are contributing factors to the growing interest in AI tax solutions. To comply with these requirements, tax professionals need a level of data granularity that forces them to access, validate, and analyze vast amounts of information—a process that AI can help accelerate.
Additionally, tax professionals require tax-sanitized data. Formatting that data properly requires the right expertise and technology, which may require the tax agency to invest in advanced analytics and integrated tools.
Reducing Human Error
Another driver of AI adoption in the tax industry is automating routine data entry and processing to eliminate human error and accelerate processing time. Likewise, AI is also being deployed to improve the accuracy of tax calculations and analyze large datasets for tax compliance.
AI tax solutions free up professionals for higher-value work by taking on manual and time-consuming tasks. Compliance with and Reporting of Corporate Taxes AI tax solutions are giving businesses new ways to simplify complex accounting processes and enhance the accuracy of corporate tax compliance and reporting.
A lot of bookkeeping and accounting tasks for businesses are also automated by AI-enhanced accounting solutions. Financial data can be securely stored and analyzed by AI solutions, which increases productivity and reduces the likelihood of error and fraud. Additionally, AI can keep an eye on tax regulations and immediately notify accountants of any changes. By continuously scanning global regulatory databases, AI systems can identify and flag any tax policy changes or updates that might impact a business’s operations. To avoid potential penalties, businesses can then make timely adjustments to their budgeting, reporting, and overall compliance strategies.
Enhanced Reporting and Compliance AI can also identify compliance gaps. These systems look at data that has to do with taxes, look for potential problems, and tell business owners to do the right thing before they get hit with penalties. Corporate expense tracking and data entry are both automated by some AI solutions. These intelligent tools significantly reduce the need for manual data entry by automatically capturing and categorizing transactions, further reducing the risk of human error and allowing accountants to focus on more strategic tasks. AI tax compliance tools can produce real-time financial reports that meet the standards of the tax industry. Businesses can use these reports throughout the year to make well-informed decisions and get ready for tax season.
Businesses operating in regions with specific tax requirements, such as the Goods and Services Tax (GST) and Business Activity Statements (BAS), can benefit from AI tools that automatically calculate the relevant taxes and ensure compliance with the most recent regulations. Compliance alerts and real-time updates are provided by these AI systems, which continuously monitor regulatory changes. AI-powered tax software is being developed by many businesses on their own, but established tax software providers are also incorporating AI into their platforms to improve corporate tax reporting and compliance. For example, Thomson Reuters ONESOURCE leverages AI to automate various aspects of tax compliance, reporting, and data management.
Tax Research and Predictive Modeling By analyzing historical, external, and non-financial data, AI solutions can use predictive modeling to identify potential income opportunities and expense reductions beyond compliance. This includes automated tax technical research. By quickly conducting multiple searches, examining relevant materials, and generating summaries, AI can save tax professionals countless hours. AI tax assistants, such as Bloomberg Tax Answers, further enhance efficiency by providing quick and precise answers to complex tax questions, along with citations to authoritative sources.
AI’s forecasting capabilities also enable businesses to identify tax planning opportunities. Companies can accurately estimate their future tax obligations and identify potential savings with predictive analytics. Businesses can simulate the financial impact of prospective tax changes or corporate decisions.
AI helps multinational corporations across multiple jurisdictions navigate complex international tax regulations. This function allows organizations to optimize cross-border transactions and manage transfer pricing risks. In a similar vein, these systems are able to look through intricate datasets and find deductions, exemptions, and incentives that human workers using manual procedures might miss. The Obstacles and Opportunities of Using AI in Tax While AI tax solutions offer numerous benefits, they come with challenges and limitations, particularly concerning data quality, security, and the indispensable role of human oversight.
Finding Experts in Tax AI It is difficult for any business to find AI developers, data engineers, and other AI-related positions due to the high demand for AI building skills. That obstacle is even more significant for the tax industry. Tax leaders know they need AI capabilities to stay competitive, but any AI talent they hire must also have tax expertise. Finding professionals who possess both is like cutting an even smaller slice of pie. While internal training programs can help close the gap, many tax professionals find that working with an AI development company is cheaper. Ninety-four percent of the Deloitte survey respondents said outsourcing gave them access to the “latest technology capabilities,” with 67% rating it as a “major/significant benefit.”
Enhancing Accuracy AI solutions can handle complex tasks, like tax forecasting and risk assessment. However, the industry is slower to deploy AI for these tasks because they require a high degree of accuracy. In the Deloitte survey, more than three-quarters of respondents stated that critical process AI tools must be accurate to at least 90%. There are two challenges to improving AI accuracy. To ensure that the AI model works properly, it must first be constructed and trained. Second, it must be fed high-quality data.
The quality of the data that AI tax applications consume is a significant factor in determining their accuracy and efficacy. Data that isn’t complete or accurate can cause problems with compliance, incorrect deduction or credit identification, and inaccurate tax calculations. The data used by AI tools must be kept accurate by tax data management systems. Data Protection Additionally, protecting sensitive financial information is of the utmost importance. Given the highly confidential nature of tax data, tax leaders have valid concerns about identity theft and unauthorized access, especially when using open-source AI platforms.
Strong encryption, secure data storage, and other security measures can mitigate these risks and build trust among users and clients. Likewise, AI development companies need to be completely transparent in how their AI algorithms handle and protect data if they want to foster confidence in their tax AI technologies.
The Need for Oversight
Even though AI is getting better, human oversight and expertise are still essential in the tax field, especially when dealing with complicated or nuanced tax issues. AI may have trouble understanding complex tax codes and regulations, as well as unique or unusual financial situations.